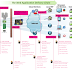
Selenium Assertions - Assert Vs Verify(Soft Assertions) Vs WaitFor
All Selenium Assertions can be used in 3 modes: "assert", "verify", and "waitFor".
When an "assert" fails, the test is aborted.
When a "verify"(Soft Assertions) fails, the test will continue execution, logging the failure. This allows a single "assert" to ensure that the application is on the correct page, followed by a bunch of "verify" assertions to test form field values, labels, etc. You don't have this facility in Selenium RC. You can implement the same using TestNG framework, select this link for custom TestNG code implemented using listeners.
"waitFor" commands wait for some condition to become true (which can be useful for testing Ajax applications). They will succeed immediately if the condition is already true. However, they will fail and halt the test if the condition does not become true within the current timeout setting (setTimeout).
---
All Selenium Assertions can be used in 3 modes: "assert", "verify", and "waitFor".
When an "assert" fails, the test is aborted.
When a "verify"(Soft Assertions) fails, the test will continue execution, logging the failure. This allows a single "assert" to ensure that the application is on the correct page, followed by a bunch of "verify" assertions to test form field values, labels, etc. You don't have this facility in Selenium RC. You can implement the same using TestNG framework, select this link for custom TestNG code implemented using listeners.
"waitFor" commands wait for some condition to become true (which can be useful for testing Ajax applications). They will succeed immediately if the condition is already true. However, they will fail and halt the test if the condition does not become true within the current timeout setting (setTimeout).
---